Transformers 文档
PoolFormer
并获得增强的文档体验
开始使用
PoolFormer

概述
PoolFormer 模型由 Sea AI Labs 在 MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision 中提出。这项工作的目标是证明 Transformer 模型的能力主要来源于其通用架构 MetaFormer,而不是设计复杂的 token 混合器以实现 SOTA 性能。
论文摘要如下:
Transformer 在计算机视觉任务中展现了巨大潜力。一个普遍的观点是,它们基于注意力的 token 混合器模块对其能力贡献最大。然而,最近的研究表明,Transformer 中基于注意力的模块可以被空间 MLP 取代,并且由此产生的模型仍然表现良好。基于这一观察,我们假设 Transformer 的通用架构,而非特定的 token 混合器模块,对模型的性能更为关键。为了验证这一点,我们特意将 Transformer 中的注意力模块替换为一个极其简单的空间池化操作符,以进行最基本的 token 混合。令人惊讶的是,我们观察到由此衍生的模型,命名为 PoolFormer,在多个计算机视觉任务中取得了具有竞争力的性能。例如,在 ImageNet-1K 上,PoolFormer 实现了 82.1% 的 top-1 准确率,在参数量减少 35%/52% 和 MACs 减少 48%/60% 的情况下,超越了经过精心调整的视觉 Transformer/MLP 类基线 DeiT-B/ResMLP-B24 分别 0.3%/1.1% 的准确率。PoolFormer 的有效性验证了我们的假设,并促使我们提出“MetaFormer”的概念,这是一种从 Transformer 中抽象出来的通用架构,但没有指定 token 混合器。基于广泛的实验,我们认为 MetaFormer 是近来 Transformer 和 MLP 类模型在视觉任务中取得优异结果的关键。这项工作呼吁未来更多的研究致力于改进 MetaFormer,而不是专注于 token 混合器模块。此外,我们提出的 PoolFormer 可以作为未来 MetaFormer 架构设计的起始基线。
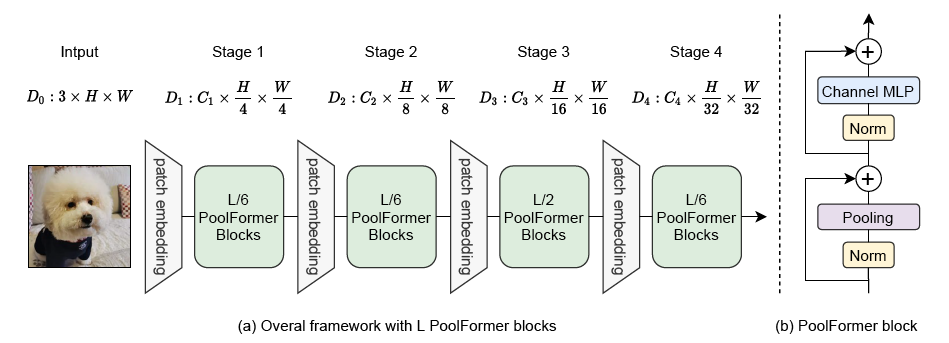
下图展示了 PoolFormer 的架构。摘自原文。
使用技巧
- PoolFormer 采用分层架构,其中注意力机制被简单的平均池化层取代。模型的所有检查点都可以在hub上找到。
- 可以使用 PoolFormerImageProcessor 来为模型准备图像。
- 与大多数模型一样,PoolFormer 有不同的大小,具体细节见下表。
| 模型变体 | 深度 | 隐藏层大小 | 参数 (M) | ImageNet-1k Top 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s12 | [2, 2, 6, 2] | [64, 128, 320, 512] | 12 | 77.2 |
| s24 | [4, 4, 12, 4] | [64, 128, 320, 512] | 21 | 80.3 |
| s36 | [6, 6, 18, 6] | [64, 128, 320, 512] | 31 | 81.4 |
| m36 | [6, 6, 18, 6] | [96, 192, 384, 768] | 56 | 82.1 |
| m48 | [8, 8, 24, 8] | [96, 192, 384, 768] | 73 | 82.5 |
资源
一个官方 Hugging Face 和社区(以🌎表示)资源列表,帮助您开始使用 PoolFormer。
- PoolFormerForImageClassification 受此示例脚本和notebook支持。
- 另请参阅:图像分类任务指南
如果您有兴趣在此处提交资源,请随时开启 Pull Request,我们将对其进行审查!该资源最好能展示一些新内容,而不是重复现有资源。
PoolFormerConfig
class transformers.PoolFormerConfig
< source 来源 >( num_channels = 3 patch_size = 16 stride = 16 pool_size = 3 mlp_ratio = 4.0 depths = [2, 2, 6, 2] hidden_sizes = [64, 128, 320, 512] patch_sizes = [7, 3, 3, 3] strides = [4, 2, 2, 2] padding = [2, 1, 1, 1] num_encoder_blocks = 4 drop_path_rate = 0.0 hidden_act = 'gelu' use_layer_scale = True layer_scale_init_value = 1e-05 initializer_range = 0.02 **kwargs )
参数
- num_channels (
int, 可选, 默认为 3) — 输入图像中的通道数。 - patch_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 16) — 输入 patch 的大小。 - stride (
int, 可选, 默认为 16) — 输入 patch 的步长。 - pool_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 3) — 池化窗口的大小。 - mlp_ratio (
float, 可选, 默认为 4.0) — MLP 输出通道数与输入通道数的比率。 - depths (
list, 可选, 默认为[2, 2, 6, 2]) — 每个编码器块的深度。 - hidden_sizes (
list, 可选, 默认为[64, 128, 320, 512]) — 每个编码器块的隐藏大小。 - patch_sizes (
list, 可选, 默认为[7, 3, 3, 3]) — 每个编码器块的输入 patch 大小。 - strides (
list, 可选, 默认为[4, 2, 2, 2]) — 每个编码器块的输入 patch 步长。 - padding (
list, 可选, 默认为[2, 1, 1, 1]) — 每个编码器块的输入 patch 填充。 - num_encoder_blocks (
int, 可选, 默认为 4) — 编码器块的数量。 - drop_path_rate (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.0) — Dropout 层的 dropout 率。 - hidden_act (
str, 可选, 默认为"gelu") — 隐藏层的激活函数。 - use_layer_scale (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否使用层缩放。 - layer_scale_init_value (
float, 可选, 默认为 1e-05) — 层缩放的初始值。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.02) — 权重的初始化范围。
这是用于存储 PoolFormerModel 配置的配置类。它用于根据指定参数实例化 PoolFormer 模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将生成与 PoolFormer sail/poolformer_s12 架构相似的配置。
配置对象继承自 PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。有关更多信息,请参阅 PretrainedConfig 的文档。
示例
>>> from transformers import PoolFormerConfig, PoolFormerModel
>>> # Initializing a PoolFormer sail/poolformer_s12 style configuration
>>> configuration = PoolFormerConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the sail/poolformer_s12 style configuration
>>> model = PoolFormerModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configPoolFormerFeatureExtractor
预处理单张或批量图像。
PoolFormerImageProcessor
class transformers.PoolFormerImageProcessor
< source 来源 >( do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None crop_pct: int = 0.9 resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BICUBIC: 3> do_center_crop: bool = True crop_size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098 do_rescale: bool = True do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None **kwargs )
参数
- do_resize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否将图像的(高度,宽度)尺寸调整到指定的size。可在preprocess方法中通过do_resize覆盖。 - size (
dict[str, int]可选, 默认为{"shortest_edge" -- 224}): 调整大小后的图像尺寸。可在preprocess方法中通过size覆盖。如果未设置 `crop_pct`:- size 为
{"height": h, "width": w}:图像将调整大小为(h, w)。 - size 为
{"shortest_edge": s}:图像的最短边将调整大小为 s,同时保持宽高比。
如果设置了 `crop_pct`:
- size 为
{"height": h, "width": w}:图像将调整大小为(int(floor(h/crop_pct)), int(floor(w/crop_pct))) - size 为
{"height": c, "width": c}:图像的最短边将调整大小为int(floor(c/crop_pct),同时保持宽高比。 - size 为
{"shortest_edge": c}:图像的最短边将调整大小为int(floor(c/crop_pct),同时保持宽高比。
- size 为
- crop_pct (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.9) — 从中心裁剪图像的百分比。可在preprocess方法中通过crop_pct覆盖。 - resample (
PILImageResampling, 可选, 默认为Resampling.BICUBIC) — 调整图像大小时使用的重采样滤波器。可在preprocess方法中通过resample覆盖。 - do_center_crop (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否对图像进行中心裁剪。如果输入大小沿任意边小于crop_size,图像将用 0 填充,然后进行中心裁剪。可在preprocess方法中通过do_center_crop覆盖。 - crop_size (
dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为{"height" -- 224, "width": 224}): 应用中心裁剪后图像的大小。仅在do_center_crop设置为True时生效。可在preprocess方法中通过crop_size参数覆盖。 - rescale_factor (
int或float, 可选, 默认为1/255) — 如果调整图像大小,则使用的缩放因子。可在preprocess方法中通过rescale_factor参数覆盖。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否通过指定比例rescale_factor重新缩放图像。可在preprocess方法中通过do_rescale参数覆盖。 - do_normalize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 控制是否对图像进行归一化。可在preprocess方法中通过do_normalize参数覆盖。 - image_mean (
float或list[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — 图像归一化时使用的均值。这是一个浮点数或浮点数列表,其长度与图像中的通道数相同。可在preprocess方法中通过image_mean参数覆盖。 - image_std (
float或list[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — 图像归一化时使用的标准差。这是一个浮点数或浮点数列表,其长度与图像中的通道数相同。可在preprocess方法中通过image_std参数覆盖。
构建 PoolFormer 图像处理器。
preprocess
< source 来源 >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None crop_pct: typing.Optional[int] = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: typing.Optional[bool] = None crop_size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None )
参数
- images (
ImageInput) — 要预处理的图像。期望单个或批量图像,像素值范围为 0 到 255。如果传入的图像像素值在 0 到 1 之间,请设置do_rescale=False。 - do_resize (
bool, 可选, 默认为self.do_resize) — 是否调整图像大小。 - size (
dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为self.size) — 应用调整大小后图像的尺寸。 - crop_pct (
float, 可选, 默认为self.crop_pct) — 图像裁剪的百分比。仅当do_resize设置为True时有效。 - resample (
int, 可选, 默认为self.resample) — 如果调整图像大小,要使用的重采样过滤器。可以是枚举PILImageResampling之一。仅当do_resize设置为True时有效。 - do_center_crop (
bool, 可选, 默认为self.do_center_crop) — 是否对图像进行中心裁剪。 - crop_size (
dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为self.crop_size) — 应用中心裁剪后图像的尺寸。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选, 默认为self.do_rescale) — 是否将图像值重新缩放至 [0 - 1] 之间。 - rescale_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为self.rescale_factor) — 如果do_rescale设置为True,则按此重新缩放图像的缩放因子。 - do_normalize (
bool, 可选, 默认为self.do_normalize) — 是否对图像进行归一化。 - image_mean (
float或list[float], 可选, 默认为self.image_mean) — 图像平均值。 - image_std (
float或list[float], 可选, 默认为self.image_std) — 图像标准差。 - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选) — 返回张量的类型。可以是以下之一:- 未设置:返回
np.ndarray列表。 TensorType.TENSORFLOW或'tf':返回tf.Tensor类型的批处理。TensorType.PYTORCH或'pt':返回torch.Tensor类型的批处理。TensorType.NUMPY或'np':返回np.ndarray类型的批处理。TensorType.JAX或'jax':返回jax.numpy.ndarray类型的批处理。
- 未设置:返回
- data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选, 默认为ChannelDimension.FIRST) — 输出图像的通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:ChannelDimension.FIRST:图像为 (num_channels, height, width) 格式。ChannelDimension.LAST:图像为 (height, width, num_channels) 格式。
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:"channels_first"或ChannelDimension.FIRST:图像为 (num_channels, height, width) 格式。"channels_last"或ChannelDimension.LAST:图像为 (height, width, num_channels) 格式。"none"或ChannelDimension.NONE:图像为 (height, width) 格式。
预处理一张或一批图像。
PoolFormerImageProcessorFast
class transformers.PoolFormerImageProcessorFast
< source >( **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.poolformer.image_processing_poolformer_fast.PoolFormerFastImageProcessorKwargs] )
构造一个快速 Poolformer 图像处理器。
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.poolformer.image_processing_poolformer_fast.PoolFormerFastImageProcessorKwargs] ) → <class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
参数
- images (
Union[PIL.Image.Image, numpy.ndarray, torch.Tensor, list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']]) — 要预处理的图像。期望单个或批量图像,像素值范围为 0 到 255。如果传入的图像像素值在 0 到 1 之间,请设置do_rescale=False。 - do_resize (
bool, 可选) — 是否调整图像大小。 - size (
dict[str, int], 可选) — 描述模型最大输入维度。 - default_to_square (
bool, 可选) — 如果尺寸为整数,调整大小时是否默认为正方形图像。 - resample (
Union[PILImageResampling, F.InterpolationMode, NoneType]) — 如果调整图像大小,要使用的重采样过滤器。可以是枚举PILImageResampling之一。仅当do_resize设置为True时有效。 - do_center_crop (
bool, 可选) — 是否对图像进行中心裁剪。 - crop_size (
dict[str, int], 可选) — 应用center_crop后输出图像的尺寸。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选) — 是否重新缩放图像。 - rescale_factor (
Union[int, float, NoneType]) — 如果do_rescale设置为True,则按此重新缩放图像的缩放因子。 - do_normalize (
bool, 可选) — 是否对图像进行归一化。 - image_mean (
Union[float, list[float], NoneType]) — 用于归一化的图像平均值。仅当do_normalize设置为True时有效。 - image_std (
Union[float, list[float], NoneType]) — 用于归一化的图像标准差。仅当do_normalize设置为True时有效。 - do_convert_rgb (
bool, 可选) — 是否将图像转换为 RGB。 - return_tensors (
Union[str, ~utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType]) — 如果设置为 `pt`,则返回堆叠的张量,否则返回张量列表。 - data_format (
~image_utils.ChannelDimension, 可选) — 仅支持ChannelDimension.FIRST。为与慢速处理器兼容而添加。 - input_data_format (
Union[str, ~image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType]) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:"channels_first"或ChannelDimension.FIRST:图像为 (num_channels, height, width) 格式。"channels_last"或ChannelDimension.LAST:图像为 (height, width, num_channels) 格式。"none"或ChannelDimension.NONE:图像为 (height, width) 格式。
- device (
torch.device, 可选) — 处理图像的设备。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断设备。 - disable_grouping (
bool, 可选) — 是否禁用按大小对图像进行分组以单独处理而不是批量处理。如果为 None,则如果图像在 CPU 上,将设置为 True,否则为 False。此选择基于经验观察,详情在此处:https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/38157 - crop_pct (
float, 可选, 默认为self.crop_pct) — 图像裁剪的百分比。仅当do_resize设置为True时有效。
返回
<class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
- data (
dict) — 由 call 方法返回的列表/数组/张量字典(“pixel_values”等)。 - tensor_type (
Union[None, str, TensorType], 可选) — 您可以在此处提供一个`tensor_type`,以便在初始化时将整数列表转换为PyTorch/TensorFlow/Numpy张量。
PoolFormerModel
class transformers.PoolFormerModel
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PoolFormerModel) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,仅加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法加载模型权重。
输出原始隐藏状态的裸 Poolformer 模型,顶部没有任何特定头部。
此模型继承自 PreTrainedModel。查看超类文档,了解库为其所有模型实现的一般方法(例如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入大小、修剪头部等)。
此模型也是 PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规 PyTorch 模块使用,并参考 PyTorch 文档中所有与一般用法和行为相关的事项。
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithNoAttention 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensor,形状为(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size),可选) — 对应于输入图像的张量。像素值可以使用{image_processor_class}获取。详情请参阅{image_processor_class}.__call__({processor_class}使用{image_processor_class}处理图像)。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。更多详情请参阅返回张量中的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回 ModelOutput 而不是普通元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithNoAttention 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithNoAttention 或一个 torch.FloatTensor 元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含根据配置 (PoolFormerConfig) 和输入的不同元素。
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor, 形状为(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor元组(如果模型有嵌入层,则为嵌入输出,+ 每个层的输出)形状为(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)。模型在每个层输出的隐藏状态以及可选的初始嵌入输出。
PoolFormerModel 的 forward 方法,覆盖了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管 forward pass 的配方需要在此函数中定义,但之后应该调用 Module 实例而不是此函数,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者则静默忽略它们。
PoolFormerForImageClassification
class transformers.PoolFormerForImageClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PoolFormerForImageClassification) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,仅加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法加载模型权重。
带图像分类头部的 PoolFormer 模型转换器
此模型继承自 PreTrainedModel。查看超类文档,了解库为其所有模型实现的一般方法(例如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入大小、修剪头部等)。
此模型也是 PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规 PyTorch 模块使用,并参考 PyTorch 文档中所有与一般用法和行为相关的事项。
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensor,形状为(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size),可选) — 对应于输入图像的张量。像素值可以使用{image_processor_class}获取。详情请参阅{image_processor_class}.__call__({processor_class}使用{image_processor_class}处理图像)。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor,形状为(batch_size,),可选) — 用于计算图像分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]之间。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失);如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。更多详情请参阅返回张量中的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回 ModelOutput 而不是普通元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention 或一个 torch.FloatTensor 元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含根据配置 (PoolFormerConfig) 和输入的不同元素。
- loss (形状为
(1,)的torch.FloatTensor,可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类损失(如果 config.num_labels==1,则为回归损失)。 - logits (形状为
(batch_size, config.num_labels)的torch.FloatTensor) — 分类(如果 config.num_labels==1,则为回归)分数(SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor元组(如果模型有嵌入层,则为嵌入输出,+ 每个阶段的输出)形状为(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)。模型在每个阶段输出的隐藏状态(也称为特征图)。
PoolFormerForImageClassification 的 forward 方法,覆盖了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管 forward pass 的配方需要在此函数中定义,但之后应该调用 Module 实例而不是此函数,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者则静默忽略它们。
示例
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, PoolFormerForImageClassification
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("sail/poolformer_s12")
>>> model = PoolFormerForImageClassification.from_pretrained("sail/poolformer_s12")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
...