开源 AI 食谱文档
结合文档检索(ColPali)和视觉语言模型(VLM)的多模态检索增强生成(RAG)
并获得增强的文档体验
开始使用
结合文档检索(ColPali)和视觉语言模型(VLM)的多模态检索增强生成(RAG)
作者: Sergio Paniego
🚨 警告:此 Notebook 资源密集,需要大量计算能力。如果您在 Colab 中运行此 Notebook,它将使用 A100 GPU。
在本 Notebook 中,我们将演示如何通过结合用于文档检索的 ColPali 检索器与 Qwen2-VL 视觉语言模型(VLM)来构建一个多模态检索增强生成(RAG)系统。这些模型共同构成了一个强大的 RAG 系统,能够通过基于文本的文档和视觉数据增强查询响应。
我们不依赖通过 OCR 提取数据的复杂文档处理器管道,而是利用文档检索模型来高效地根据特定用户查询检索相关文档。
我还建议您查看并收藏 smol-vision 存储库,该存储库启发了本 Notebook——尤其是这个 Notebook。有关 RAG 的介绍,您可以查看这本食谱!
此图灵感来源于 Aymeric Roucher 在 高级 RAG 或 RAG 评估食谱中的工作。
1. 安装依赖
让我们开始安装项目所需的基本库!🚀
!pip install -U -q byaldi pdf2image qwen-vl-utils transformers
# Tested with byaldi==0.0.4, pdf2image==1.17.0, qwen-vl-utils==0.0.8, transformers==4.45.0我们还将安装 poppler-utils 以方便 PDF 操作。此实用程序提供处理 PDF 文件所需的基本工具,确保我们能够高效地处理项目中的任何文档相关任务。
!sudo apt-get install -y poppler-utils
2. 加载数据集 📁
在本节中,我们将使用宜家组装说明作为数据集。这些 PDF 包含组装各种家具的分步指南。想象一下,在组装新宜家家具时能够向我们的助手寻求帮助!🛋
要下载组装说明,您可以按照这些步骤。
对于本 Notebook,我选择了一些示例,但在实际场景中,我们可以处理大量 PDF 以增强模型的功能。
import requests
import os
pdfs = {
"MALM": "https://www.ikea.com/us/en/assembly_instructions/malm-4-drawer-chest-white__AA-2398381-2-100.pdf",
"BILLY": "https://www.ikea.com/us/en/assembly_instructions/billy-bookcase-white__AA-1844854-6-2.pdf",
"BOAXEL": "https://www.ikea.com/us/en/assembly_instructions/boaxel-wall-upright-white__AA-2341341-2-100.pdf",
"ADILS": "https://www.ikea.com/us/en/assembly_instructions/adils-leg-white__AA-844478-6-2.pdf",
"MICKE": "https://www.ikea.com/us/en/assembly_instructions/micke-desk-white__AA-476626-10-100.pdf",
}
output_dir = "data"
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
for name, url in pdfs.items():
response = requests.get(url)
pdf_path = os.path.join(output_dir, f"{name}.pdf")
with open(pdf_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"Downloaded {name} to {pdf_path}")
print("Downloaded files:", os.listdir(output_dir))下载组装说明后,我们将 PDF 转换为图像。此步骤至关重要,因为它允许文档检索模型(ColPali)有效地处理和操作视觉内容。
import os
from pdf2image import convert_from_path
def convert_pdfs_to_images(pdf_folder):
pdf_files = [f for f in os.listdir(pdf_folder) if f.endswith(".pdf")]
all_images = {}
for doc_id, pdf_file in enumerate(pdf_files):
pdf_path = os.path.join(pdf_folder, pdf_file)
images = convert_from_path(pdf_path)
all_images[doc_id] = images
return all_images
all_images = convert_pdfs_to_images("/content/data/")让我们可视化一个示例组装指南,了解这些说明是如何呈现的!这将帮助我们了解将要处理的内容的格式和布局。👀
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 8, figsize=(15, 10))
>>> for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
... img = all_images[0][i]
... ax.imshow(img)
... ax.axis("off")
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>> plt.show()3. 初始化 ColPali 多模态文档检索模型 🤖
数据集准备就绪后,我们将初始化文档检索模型,该模型将负责从原始图像中提取相关信息,并根据我们的查询提供适当的文档。
通过利用此模型,我们可以显著增强我们的对话能力。
对于此任务,我们将使用 Byaldi。开发者将该库描述为:“Byaldi 是 RAGatouille 的迷你姐妹项目。它是一个围绕 ColPali 存储库的简单包装器,旨在使 ColPALI 等后期交互多模态模型易于使用熟悉的 API。”
在此项目中,我们将专门关注 ColPali。
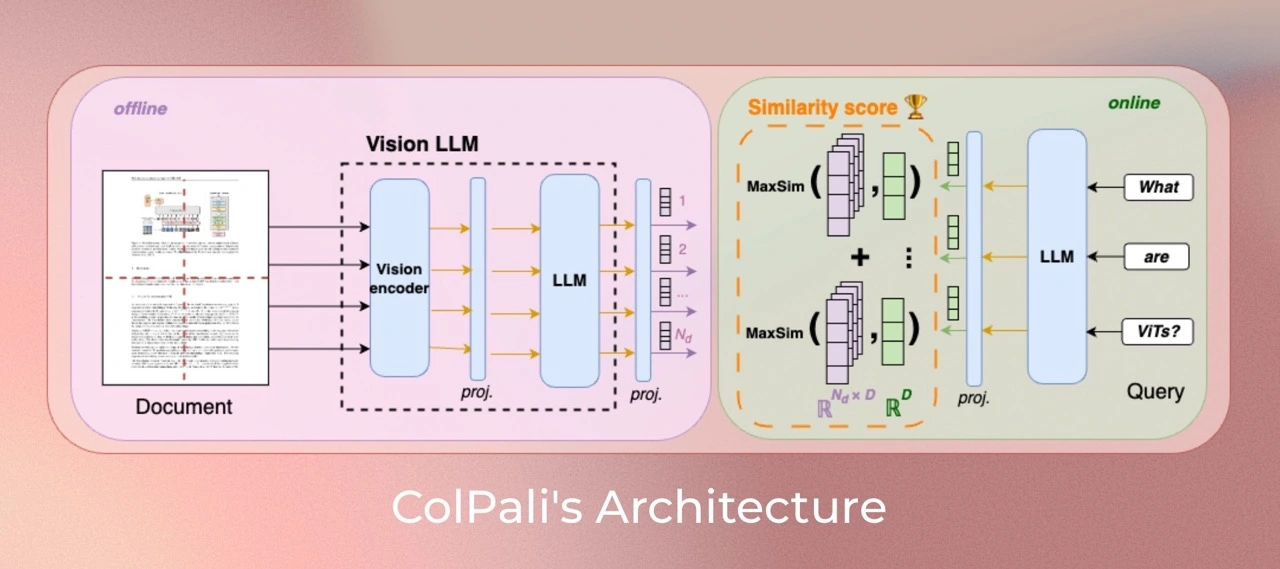
此外,您可以探索 ViDore(视觉文档检索基准),查看表现最佳的检索器。
首先,我们将从检查点加载模型。
from byaldi import RAGMultiModalModel
docs_retrieval_model = RAGMultiModalModel.from_pretrained("vidore/colpali-v1.2")接下来,我们可以使用文档检索模型直接索引文档,方法是指定存储 PDF 的文件夹。这将允许模型处理和组织文档,以便根据我们的查询进行高效检索。
docs_retrieval_model.index(
input_path="data/", index_name="image_index", store_collection_with_index=False, overwrite=True
)4. 使用文档检索模型检索文档 🤔
初始化文档检索模型后,我们现在可以通过提交用户查询并检查它检索到的相关文档来测试其功能。
模型将直接按与查询的相关性对结果进行排名并返回。
让我们试一试!
text_query = "How many people are needed to assemble the Malm?"
results = docs_retrieval_model.search(text_query, k=3)
results现在,让我们检查模型检索到的特定文档(图像)。这将使我们能够查看与查询对应的视觉内容,并了解模型如何选择相关信息。
def get_grouped_images(results, all_images):
grouped_images = []
for result in results:
doc_id = result["doc_id"]
page_num = result["page_num"]
grouped_images.append(
all_images[doc_id][page_num - 1]
) # page_num are 1-indexed, while doc_ids are 0-indexed. Source https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/byaldi?tab=readme-ov-file#searching
return grouped_images
grouped_images = get_grouped_images(results, all_images)让我们仔细查看检索到的文档,以了解它们包含的信息。此检查将帮助我们评估检索到的内容与查询相关的准确性和质量。
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 10))
>>> for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
... img = grouped_images[i]
... ax.imshow(img)
... ax.axis("off")
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>> plt.show()5. 初始化视觉语言模型用于问答 🙋
接下来,我们将初始化用于问答的视觉语言模型 (VLM)。在这种情况下,我们将使用 Qwen2_VL。

您可以在此处查看 Open VLM 的排行榜,了解最新进展。
首先,我们将从预训练检查点加载模型,并将其移动到 GPU 以获得最佳性能。在此处查看模型:此处。
from transformers import Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration, Qwen2VLProcessor
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
import torch
vl_model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
vl_model.cuda().eval()接下来,我们将初始化 VLM 处理器。在此步骤中,我们指定最小和最大像素大小,以优化更多图像拟合到 GPU 内存中。
有关优化图像分辨率以提高性能的更多详细信息,您可以参考此处的文档。
min_pixels = 224 * 224
max_pixels = 1024 * 1024
vl_model_processor = Qwen2VLProcessor.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", min_pixels=min_pixels, max_pixels=max_pixels
)6. 组装 VLM 模型并测试系统 🔧
所有组件加载完毕后,我们现在可以组装系统进行测试。首先,我们将通过向系统提供三张检索到的图像以及用户查询来创建聊天结构。此步骤可以根据您的具体需求进行定制,从而在与模型交互时具有更大的灵活性!
chat_template = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
"image": grouped_images[0],
},
{
"type": "image",
"image": grouped_images[1],
},
{
"type": "image",
"image": grouped_images[2],
},
{"type": "text", "text": text_query},
],
}
]现在,让我们应用这个聊天结构。
text = vl_model_processor.apply_chat_template(chat_template, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)接下来,我们将处理输入,以确保它们格式正确并准备好用作视觉语言模型 (VLM) 的输入。此步骤对于使模型能够根据提供的数据有效生成响应至关重要。
image_inputs, _ = process_vision_info(chat_template)
inputs = vl_model_processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")我们现在准备好生成答案了!让我们看看系统如何利用处理后的输入,根据用户查询和检索到的图像提供响应。
generated_ids = vl_model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=500)模型生成输出后,我们对其进行后处理以生成最终答案。
generated_ids_trimmed = [out_ids[len(in_ids) :] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)]
output_text = vl_model_processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)>>> print(output_text[0])The Malm requires two people to assemble it.
7. 全部组装起来!🧑🏭️
现在,让我们创建一个包含整个管道的方法,以便将来可以轻松地重复使用它。
def answer_with_multimodal_rag(
vl_model, docs_retrieval_model, vl_model_processor, grouped_images, text_query, top_k, max_new_tokens
):
results = docs_retrieval_model.search(text_query, k=top_k)
grouped_images = get_grouped_images(results, all_images)
chat_template = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [{"type": "image", "image": image} for image in grouped_images]
+ [{"type": "text", "text": text_query}],
}
]
# Prepare the inputs
text = vl_model_processor.apply_chat_template(chat_template, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(chat_template)
inputs = vl_model_processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
# Generate text from the vl_model
generated_ids = vl_model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens)
generated_ids_trimmed = [out_ids[len(in_ids) :] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)]
# Decode the generated text
output_text = vl_model_processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
return output_text让我们看看完整的 RAG 系统是如何运行的!
>>> output_text = answer_with_multimodal_rag(
... vl_model=vl_model,
... docs_retrieval_model=docs_retrieval_model,
... vl_model_processor=vl_model_processor,
... grouped_images=grouped_images,
... text_query="How do I assemble the Micke desk?",
... top_k=3,
... max_new_tokens=500,
... )
>>> print(output_text[0])To assemble the Micke desk, follow these steps: 1. **Prepare the Components**: Lay out all the components of the desk on a flat surface. 2. **Attach the Legs**: Place the legs on the bottom of the desk frame. Ensure they are securely attached. 3. **Attach the Top**: Place the top of the desk on the frame, making sure it is level and stable. 4. **Secure with Screws**: Use the provided screws to secure the top to the frame. Ensure all screws are tightened securely. 5. **Final Check**: Double-check that all parts are properly attached and the desk is stable. Refer to the detailed instructions provided in the image for specific steps and any additional information needed for assembly.
🏆 我们现在拥有一个功能齐全的 RAG 管道,它利用了文档检索模型和视觉语言模型!这种强大的组合使我们能够根据用户查询和相关文档生成富有洞察力的响应。
8. 继续旅程 🧑🎓️
本食谱只是探索多模态 RAG 系统潜力的起点。如果您渴望深入了解,这里有一些想法和资源可以指导您的下一步
🔍 使用 ColPali 进一步探索:
📖 拓展阅读:
💡 有用集合:
📝 论文和原始代码:
在您继续探索多模态检索和生成系统世界的同时,请随意探索这些资源!
< > 在 GitHub 上更新